Russia’s bold plan to build eight nuclear plants in Iran further cements their alliance against America while openly defying Western sanctions and nuclear nonproliferation efforts.
Key Takeaways
- Russia has signed a contract to construct eight nuclear power plants in Iran, with four planned for the southern province of Bushehr
- Construction is already underway on Units 2 and 3 at the existing Bushehr Nuclear Power Plant, marking significant progress in the initiative
- Russia will supply nuclear fuel for Iran’s 1,000-megawatt reactor for ten years, with spent fuel returning to Russia to prevent plutonium separation
- This development represents a deepening of Iran-Russia military and energy cooperation, especially following their collaboration during the Ukraine conflict
- The Biden administration has remained notably silent on this provocative expansion of Iran’s nuclear capabilities
Russia-Iran Nuclear Partnership Expands
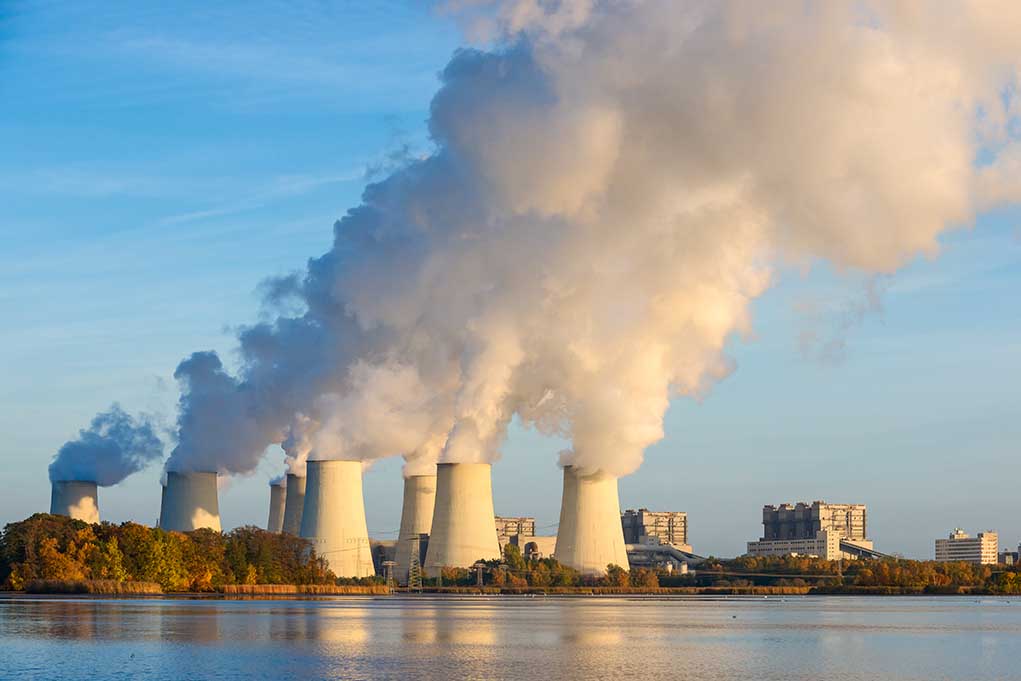
The Atomic Energy Organization of Iran (AEOI) has confirmed Russia’s commitment to build eight nuclear power plants across Iran, significantly expanding the Islamic Republic’s nuclear capabilities. Mohammad Eslami, President of the AEOI, announced the ambitious plan that will see four reactors constructed in the southern province of Bushehr, where Iran’s only operational nuclear power facility currently stands. This massive expansion comes as both countries face intense Western sanctions, demonstrating their determination to strengthen mutual ties while openly defying American foreign policy objectives in the Middle East.
“Russia is contracted to build eight nuclear power plants in Iran, including four in the southern city of Bushehr,” stated Ebrahim Rezaei, according to the Zero Hedge.
The Bushehr Nuclear Power Plant, completed by Russia in 2011, has been central to Iran’s civilian nuclear energy program for over a decade. Construction is already underway on Units 2 and 3 at this facility, with Iranian companies leading the work. This expansion aligns with Iran’s strategic goal of tripling its nuclear power generation capacity, creating a concerning level of nuclear infrastructure development in a nation that has repeatedly threatened America’s key regional ally, Israel.
What does this mean for the potentiality of a deal? Will this be the edge Trump needs to ratchet down tensions in the ME and buy time for the US to rebuild its economy or is this just another stumbling block? https://t.co/yX96v16ywu
— Brandon Weichert (@WeTheBrandon) June 9, 2025
Strategic Implications for Global Security
This nuclear cooperation extends beyond mere energy production, reflecting a broader “comprehensive strategic partnership” between Moscow and Tehran. Russia has positioned itself as a mediator between the United States and Iran on uranium enrichment discussions, further undermining American influence in the region. The timing of this announcement is particularly significant, following increased military cooperation between the two nations during the Ukraine conflict, where Iranian drones have been used extensively against Ukrainian targets.
“Iran is expanding its Bushehr nuclear power plant by building the second and third units of the facility,” stated the Arms Control Association, as reported by Zero Hedge.
Under the agreement, Russia will supply Iran with nuclear fuel for a 1,000-megawatt reactor for ten years. Critically, the spent fuel will be returned to Russia, ostensibly to prevent Iran from separating plutonium for weapons development. However, this arrangement does little to address concerns about Iran’s uranium enrichment activities at other facilities. The Biden administration has remained conspicuously silent on this development, continuing its pattern of weakness in confronting Iranian nuclear ambitions.
Challenges and Skepticism
Despite the grandiose announcements, critics point to Russia’s history of taking substantial funds from Iran for nuclear projects while making limited actual progress. The current Bushehr expansion has already faced significant delays, raising questions about the timeline for completing eight additional reactors. These concerns are amplified by the complex technical challenges involved and the impact of international sanctions on both countries, which restrict access to critical components and technologies needed for advanced nuclear facilities.
“Russia to build EIGHT nuclear power plants in Iran — Tehran’s National Security spox,” stated spokesperson, Tehran’s National Security. as noted by Zero Hedge.
Both countries claim the expansion adheres to International Atomic Energy Agency standards, but the growing nuclear cooperation between these anti-American regimes raises serious concerns about proliferation risks. As Russia and Iran continue to strengthen their alliance through energy cooperation, military support, and diplomatic coordination, they create a formidable axis of resistance against Western interests. This partnership, bolstered by their relationships with other BRICS nations, enables both countries to circumvent sanctions and sustain their military-industrial capabilities despite international pressure.
America’s National Security at Risk
The expansion of Iran’s nuclear infrastructure under Russian guidance represents a clear threat to American interests and regional stability. With President Trump now returning to office, he faces the challenge of addressing this growing nuclear threat after years of Biden’s appeasement policies emboldened both Iran and Russia. The Trump administration will need to develop a comprehensive strategy to counter this alliance, potentially including enhanced sanctions, strengthened support for regional allies like Israel, and a more assertive posture toward nuclear proliferation threats from rogue regimes.
This nuclear collaboration between Russia and Iran highlights the consequences of weak American leadership on the world stage. As these authoritarian regimes deepen their cooperation, they present an increasingly coordinated challenge to American influence and Western security interests. The construction of these eight nuclear plants will provide Iran with expanded nuclear expertise, infrastructure, and potentially create new pathways to nuclear weapons capability under the guise of civilian energy production.